Beitrag • 8 Min. Lesezeit
Was ist Incident Management? Arten und Lösungen erklärt
Entdecken Sie erprobte Frameworks, um IT-Störungen zu identifizieren, darauf zu reagieren und sie zu verhindern – und gleichzeitig ein stärkeres, widerstandsfähigeres IT-Team aufzubauen.
Zuletzt aktualisiert: 5. September 2025
Was ist Incident Management?Unter Incident Management versteht man einen strukturierter Ansatz zur Reaktion auf ungeplante Störungen oder Verschlechterungen von IT-Services, mit dem Ziel, den Normalbetrieb so schnell wie möglich wiederherzustellen. Effektives Incident Management umfasst:
Es umfasst die Prozesse, Rollen und Tools, die zur Identifizierung, Analyse und Lösung technischer Probleme verwendet werden, während die Auswirkungen auf Geschäftsabläufe und Kund:innen minimiert werden. |
Es ist ein allzu häufiges Szenario: Ihr Team nähert sich dem Ende eines zeitaufwändigen Produktrollouts, als Ihr Kerndienst abstürzt. Kund:innen können sich nicht anmelden, interne Teams sind blockiert und alle suchen nach Antworten. Incident Management ist die Art, wie Unternehmen diese schlimmsten Szenarien beheben.
Vorfallmanagement ist der strukturierte Prozess zur Identifizierung, Bewertung und Lösung von IT-Service-Störungen. Es gilt für alles von einer trägen Anwendung bis hin zu einem kompletten Ausfall. Im IT Service Management (ITSM) geht es bei dieser Disziplin nicht nur um schnelle Reparaturen. Es ist ein Fundament für operative Stabilität, das Kundenvertrauen schaffen oder zerstören kann.
Erkunden Sie alle wichtigen Aspekte eines zuverlässigen Incident Management Systems, wie Best Practices und unverzichtbare Helpdesk-Metriken zur Verbesserung des Vorfallmanagement, unten.
Mehr in diesem Leitfaden:
- Warum ist Incident Management entscheidend für effektiven Service?
- Arten von Incident Management
- 6 Schritte des Incident Management Frameworks
- Best Practices für umfassendes Incident Management
- Tools und Automatisierung für Incident Management
- Wichtige Metriken zur Verfolgung der Incident Management Effektivität
- Häufig gestellte Fragen
- Vorfälle schneller mit Zendesk lösen
Warum ist Incident Management entscheidend für effektiven Service?
Wenn etwas kaputt geht, zählt jede Sekunde. Ob es sich um ein Anmeldeproblem handelt, das Mitarbeiter:innen am Arbeiten hindert, oder um einen Fehler, der Kund:innen frustriert – Geschwindigkeit und Klarheit sind entscheidend.
Starkes Vorfallmanagement ermöglicht es Teams, die Kontrolle über die Situation zu übernehmen, Services schnell wiederherzustellen und eine hohe Qualität des Kundenservice aufrechtzuerhalten, auch unter Druck. Aber die Vorteile gehen weit über das bloße Reparieren von Dingen hinaus, wenn sie kaputt gehen. Hier sind einige der wichtigsten Vorteile, die Sie von einer großartigen Incident Management Lösung erwarten können:
Incident Management Funktion | Warum es wichtig ist |
Geschäftskontinuität und Umsatzschutz | Für digital-first Kundenservice Unternehmen bedeuten Ausfallzeiten verlorene Umsätze. Starkes Vorfallmanagement (Incident Management) ist entscheidend für die schnelle Eindämmung von Störungen, insbesondere für E-Commerce und SaaS, die 24/7-Verfügbarkeit benötigen. |
Customer Experience und Kundenbindung | Die Behandlung von Vorfällen beeinflusst die Kundenwahrnehmung. Wenn Sie Situationen transparent handhaben und sie schnell lösen, werden Kund:innen gelegentliche technische Probleme verzeihen. Effektives Incident Management kommuniziert Status, Zeitpläne und Nachverfolgung. |
Mitarbeiterproduktivität und Moral | Interne IT-Vorfälle frustrieren nicht nur Mitarbeiter:innen. Sie können die Produktivität vollständig zum Entgleisen bringen. Wenn Tools und Anwendungen versagen, werden Teams untätig. Vorfallmanagement stellt Abläufe schnell wieder her und hält Mitarbeiter:innen auf ihre Verantwortlichkeiten fokussiert. |
Regulatorische Compliance und Risikomanagement | Strenge Vorschriften in Branchen wie Gesundheitswesen, Finanzwesen und Regierung schreiben spezifische Reaktionszeiten und Dokumentation für Service-Verfügbarkeit und Vorfallreaktion vor. Strukturiertes Incident Management hilft Organisationen, diese zu erfüllen, und reduziert Straf- und Compliance-Verletzungsrisiken. |
Lern- und Verbesserungsmöglichkeiten | Vorfälle bieten Lernmöglichkeiten. Ausgereiftes Incident Management umfasst Post-Incident-Reviews für kontinuierliche Verbesserung, Verhinderung zukünftiger Probleme und den Aufbau widerstandsfähiger Systeme. |
Arten von Incident Management
 |
Vorfallmanagement nimmt verschiedene Formen an, abhängig davon, wie eine Organisation arbeitet. Hier ist eine Aufschlüsselung der häufigsten Modelle:
IT Service Management (ITSM) | Ein traditioneller Helpdesk-Ansatz, ITSM Incident Management verwendet strukturierte Ticketsysteme und Prozesse zur Behandlung von Service-Störungen. Es umfasst detaillierte Dokumentation, Genehmigungsworkflows und strukturierte Eskalationsverfahren, was es effektiv für Organisationen mit komplexen Compliance-Anforderungen oder großen IT-Infrastrukturen macht. |
DevOps Incident Management | Ein schnelles, kollaboratives Modell für DevOps-Teams, das Echtzeit-Monitoring und Automatisierung für Systemstabilität betont. Dieser Ansatz priorisiert schnelle Reaktion und Lernen aus Fehlern, oft durch schuldfreie Post-Mortems, automatisierte Alarme und selbstheilende Systeme. Er opfert etwas Formalität für Geschwindigkeit, sodass er kürzere Reaktionszeiten hat. |
Major Incident Management | Ein hochstufiges Reaktionsmodell für weitreichende Probleme, die viele Nutzer:innen oder kritische Geschäftsabläufe betreffen und oft teamübergreifende Koordination erfordern. Es umfasst spezialisierte Kommunikation, die aktiviert wird, wenn normale Prozesse unzureichend sind. Es beinhaltet Führungsbriefings, Kundenkommunikation und Post-Incident Geschäftsauswirkungsbewertungen. |
Business Continuity Incident Management | Ein Aspekt der Disaster Recovery, dieses Modell behandelt Ereignisse wie Cyberangriffe, Naturkatastrophen oder Systemausfälle. Es umfasst IT, Geschäftsabläufe, HR und externe Stakeholder:innen. Es beinhaltet alternative Arbeitsplätze und Backup-Kommunikation, um sicherzustellen, dass wesentliche Geschäftsfunktionen trotz primärer Systemunavailabilität fortgesetzt werden. |
Jeder Ansatz hat seine Stärken und ist für unterschiedliche organisatorische Bedürfnisse geeignet. Viele Unternehmen verwenden ein Hybridmodell und wenden verschiedene Incident Management Arten basierend auf der Schwere und dem Umfang jedes Vorfalls an.
6 Schritte des Incident Management Frameworks
Die Vorfallreaktion folgt typischerweise einer wiederholbaren Struktur. So handhaben Teams Vorfälle von Anfang bis Ende.
1. Erkennen und identifizieren
Probleme werden oft über Monitoring-Tools oder Support-Tickets erkannt. Lösungen wie Zendesk verwenden KI, um alle Tickets und Interaktionen zu analysieren, um Probleme zu erfassen, bevor sie sich zu größeren Problemen entwickeln.
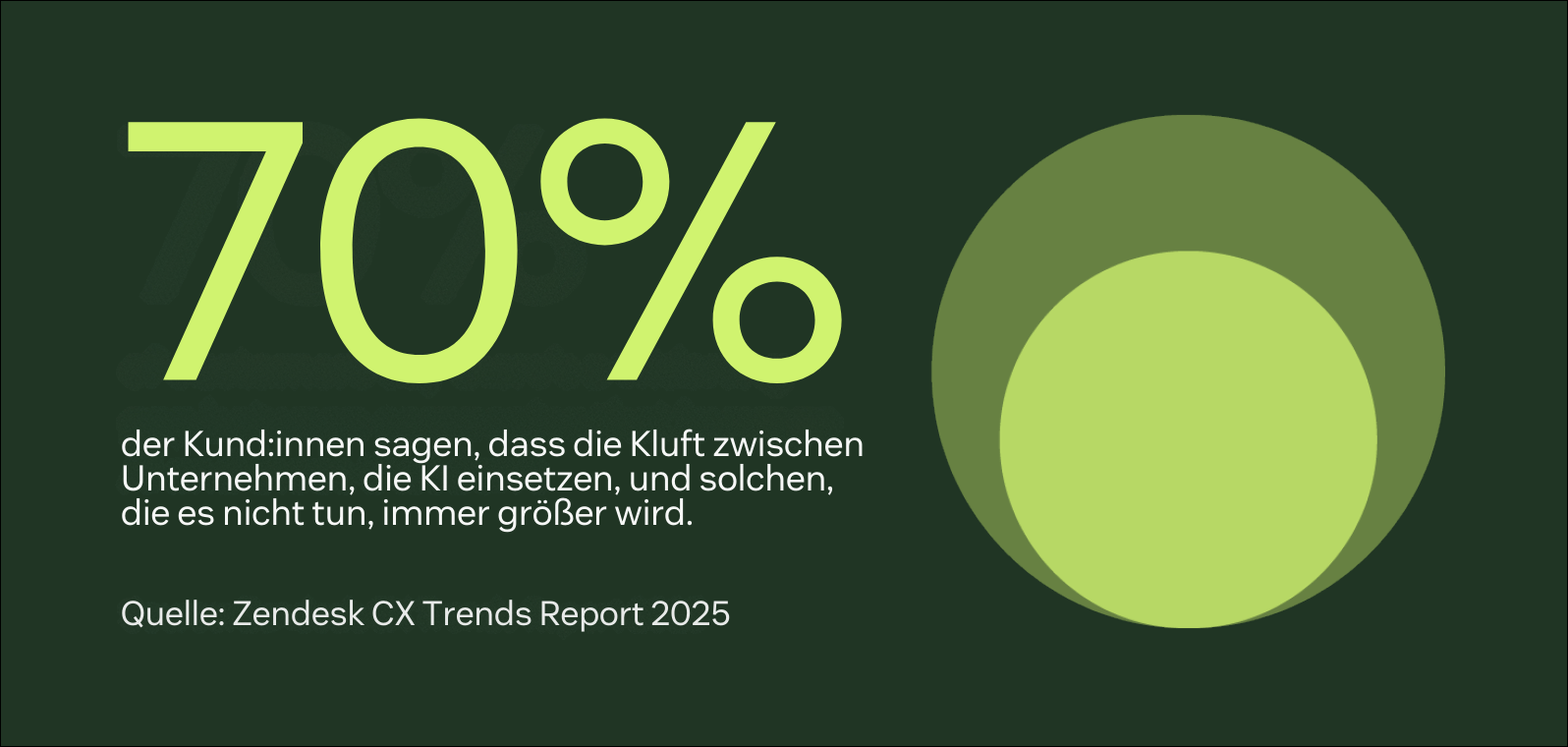 |
Frühe Erkennung ist entscheidend zur Minimierung der Auswirkungen eines Problems, mit Schritten wie:
KI oder automatisierte Systemüberwachung
Nutzermeldungen
Synthetische Transaktionsüberwachung
Proaktive Gesundheitschecks
KI und maschinelles Lernen identifizieren auch Anomalien und sagen potenzielle Probleme in Echtzeit voraus, wodurch Teams proaktiv an einer Lösung arbeiten können.
2. Aufzeichnen und klassifizieren
Vorfälle werden protokolliert und nach Schweregrad, Dringlichkeit und Auswirkung klassifiziert, um Aufgaben zu priorisieren und Ressourcen zuzuteilen. Die Klassifizierung berücksichtigt Dinge wie die am meisten betroffenen:
Nutzer:innen
Gesamtgeschäftsfunktionen
Finanzielle Auswirkungen
Prioritätsstufen (P1–P4) und Schweregradkategorien (Kritisch–Niedrig) sind häufige Wege zur Kennzeichnung dieser Klassifizierungen. Genaue Klassifizierung bestimmt Reaktionszeiten, Eskalation und mehr und hat standardisierte Kriterien für Konsistenz über Probleme hinweg.
 |
KI-gestützte Systeme können Vorfälle automatisch basierend auf historischen Daten und Inhaltsanalyse klassifizieren, menschliche Fehler reduzieren und die anfängliche Reaktion beschleunigen. KI-Agenten zum Beispiel sind intelligente Bots, die Ticketinhalte analysieren und sofort angemessene Prioritätsstufen zuweisen können.
3. Tiefer graben und diagnostizieren
Teams analysieren das Problem, indem sie Systemlogs und Fehlermeldungen überprüfen, um die Grundursache zu bestimmen. Diese investigative Phase umfasst oft mehrere Teammitglieder mit verschiedenen Fachbereichen.
Diagnosetechniken umfassen:
Log-Analyse
Systemleistungsüberwachung
Datenbankabfragen
Problem in Testumgebungen nachstellen
Für eine effektive Diagnose benötigen Sie sowohl technische Fähigkeiten als auch Zugang zu umfassenden Daten. KI-gestützte Vorfallmanagement-Software sammelt kontinuierlich Daten, um die klarstmöglichen Einblicke in Probleme und mögliche Diagnosen zu geben.
4. Eskalieren
Komplexe Probleme oder solche außerhalb der Team-Expertise werden an spezialisierte Gruppen oder externe Anbieter eskaliert.
Eskalation sollte schnell erfolgen, um Verzögerungen zu vermeiden, ausgelöst durch Überschreitung der Reaktionszeit oder Bedarf an eingeschränktem Systemzugang oder Anbieter-Support. Effektive Eskalation erfordert klare Übergabe, vollständige Dokumentation und kontinuierliche Überwachung durch den ursprünglichen Responder.
5. Lösen und wiederherstellen
Nach Identifizierung der Ursache wendet das Team eine Lösung an und stellt Services wieder her, kommuniziert den Fortschritt an betroffene Nutzer:innen. Lösung könnte umfassen
Patches
Neustarts
Rollbacks
Workarounds
Insgesamt konzentriert sich die Lösung auf schnelle Wiederherstellung und minimale Störung. Wiederherstellung umfasst die Überprüfung der Reparatur und Überwachung der Systeme, um Wiederauftreten zu verhindern.
6. Schließen und überprüfen
Nach der Lösung führen Teams eine Post-Incident-Review durch, um das Ereignis zu dokumentieren und Erfolge und Verbesserungsbereiche zu notieren.
Diese zeitnahe Überprüfung umfasst:
Zeitlinienanalyse
Grundursache
Prozesseffektivität
Empfehlungen
Sie schafft wertvolles Organisationswissen, um zukünftige Vorfälle zu verhindern und die Reaktion zu verbessern.
Best Practices für umfassendes Incident Management
Hochleistungsteams folgen einigen Best Practices, um ihre Vorfallreaktion effizient und widerstandsfähig zu halten:
- Bereiten Sie Ihr Team im Voraus vor: Klären Sie Rollen, führen Sie regelmäßige Schulungen durch und dokumentieren Sie Verfahren. Genau wie bei Feuerwehren reduzieren regelmäßige Übungen die Reaktionszeit und den Stress während Vorfällen.
- Halten Sie klare Kommunikation aufrecht: Kommunikation während eines Vorfalls sollte zeitnah und konsistent sein – auch wenn Sie noch keine Reparatur haben – weil regelmäßige Updates helfen, Vertrauen bei Nutzer:innen aufzubauen. Verwenden Sie Statusseiten, E-Mail und soziale Medien für externe Updates. Intern etablieren Sie dedizierte Kanäle für Reaktion, klare Eskalation und regelmäßige Führungsupdates.
- Dokumentieren Sie effektive Reaktionen: Dokumentieren Sie in Playbooks und Runbooks, um Teams zu helfen, schnell zu handeln und während Hochdrucksituationen ausgerichtet zu bleiben. Diese sollten schrittweise Verfahren, Kontakte, Systemzugriffsdetails und Troubleshooting-Guides für die konsistente Reaktionsqualität enthalten.
- Führen Sie gründliche Post-Incident-Reviews durch: Alle Vorfälle benötigen eine Post-Review, um Verbesserungen und Lehren zu identifizieren. Fokussieren Sie sich auf den Prozess, nicht auf Schuldzuweisungen. Effektive Reviews identifizieren systemische Probleme und resultieren in klaren Aktionspunkten zu ihrer Lösung.
- Implementieren Sie kontinuierliche Verbesserung: Analysieren Sie Vorfalldaten, um Muster und systemische Probleme zu erkennen. Dieser datengetriebene Ansatz baut widerstandsfähigere Systeme auf, indem er wiederkehrende Probleme und Lücken aufdeckt.
Während starke Prozesse und Praktiken das Fundament eines effektiven Vorfallmanagements bilden, können die richtigen Tools den Unterschied zwischen einer chaotischen Reaktion und einer koordinierten Lösung ausmachen.
Tools und Automatisierung für Incident Management
Statten Sie Ihr Team mit den richtigen Tools für eine signifikante Verbesserung aus, wie Sie Vorfälle verwalten und lösen:
- Incident Response Plattformen: Diese Plattformen bringen alle Alarme und Aktionspunkte an einem Ort zusammen und machen es einfacher, Aufgaben zuzuweisen und den Fortschritt eines Vorfalls von Anfang bis Ende zu überwachen.
- Monitoring- und Alarm-Tools: Scannen proaktiv Ihre Systeme nach Anzeichen von Problemen und senden Alarme, damit Ihr Team reagieren kann, bevor Nutzer:innen überhaupt ein Problem bemerken.
- Kommunikations- und Kollaborationssoftware: Systeme wie Slack oder Microsoft Teams ermöglichen es Teams, in Echtzeit zusammenzuarbeiten und die Verwirrung zu eliminieren, die oft die Reaktion verlangsamt.
- Statusseiten-Systeme: Diese Systeme helfen Ihnen, interne Teams und externe Nutzer:innen mit Live-Updates über Ausfälle oder Service-Änderungen informiert zu halten.
- Bereitschaftsdienst-Managementlösungen: Dies nimmt das Rätselraten darüber weg, wer verfügbar ist, indem Personal geplant und rotiert wird, um sicherzustellen, dass immer jemand bereit ist zu reagieren.
- Runbooks und Dokumentationssysteme: Diese bieten vorgeschriebene, schrittweise Anweisungen, denen sogar neue Teammitglieder während eines riskanten Vorfalls folgen können.
- Post-Mortem- und Analyse-Tools: Schauen Sie nach einem Vorfall auf KI-gestützte Kundenservice-Berichte mit Echtzeitanalysen, um Trends zu identifizieren, zukünftige Vorfallarten vorherzusagen und umsetzbare Einblicke für Prozessverbesserung zu bieten.
- Automatisierungs- und Orchestrierungsplattformen: Beschleunigen Sie die Reaktionszeit, indem Sie voreingestellte Aufgaben ausführen, Traffic umleiten oder Skripte ohne manuellen Eingriff starten.
- Helpdesks und Service Desks: Halten Sie Ihre Vorfälle organisiert, indem Sie Probleme protokollieren, sie den richtigen Personen zuweisen und sie bis zur Lösung verfolgen.
- Grundursachenanalyse-Software: Identifizieren Sie die tieferen Probleme hinter wiederkehrenden Vorfällen, sodass Sie das Problem an seiner Quelle beheben können, nicht nur die Symptome.
Die richtige Kombination von Tools kann Ihre Vorfallreaktion von reaktiver Feuerwehr zu proaktiver Problemlösung transformieren, aber Erfolg hängt letztendlich davon ab, wie gut Sie Ihre Leistung messen und optimieren.
Wichtige Metriken zur Verfolgung der Incident Management Effektivität
Die Verfolgung der richtigen Leistungsmetriken hilft Teams, ihren Ansatz zu optimieren und den Wert des Incident Managements zu beweisen:
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) misst, wie schnell Ihr Team sich eines Problems bewusst wird, nachdem es beginnt.
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) berechnet die durchschnittliche Zeit, die Ihr Team braucht, um das Problem anzugehen, sobald es identifiziert wurde.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR) Rate zeigt, wie oft Ihr Team Probleme beim ersten Versuch beheben kann, ohne zu eskalieren.
- Vorfallvolumen verfolgt die Anzahl der Vorfälle über einen bestimmten Zeitraum, was Ihnen helfen kann, neue Risiken oder Systeminstabilität zu identifizieren.
- Vorfallwiederholungsrate zeigt auf, ob ähnliche Probleme immer wieder auftauchen, und deutet darauf hin, dass Grundursachen möglicherweise noch Aufmerksamkeit benötigen.
- Kundenzufriedenheit (CSAT) spiegelt wider, wie Nutzer:innen den Lösungsprozess empfinden, oft durch Post-Incident-Umfragen gesammelt.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) Compliance Rate misst, wie konsistent Ihr Team die Reaktions- und Lösungszeiten erfüllt, die Nutzer:innen oder Klient:innen versprochen wurden.
Die konsistente Verfolgung dieser Metriken kann Ihnen helfen, Ihre Vorfallreaktion über Zeit zu verbessern und besser ausgerüstet zu sein, um häufige Fragen über Ihren Incident Management Ansatz zu beantworten.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Vorfälle schneller mit Zendesk lösen
Die Einsätze sind hoch: IT-Ausfallzeiten sind unerschwinglich teuer für Unternehmen jeder Größe und können den Markenruf langfristig schädigen. Wenn gut ausgeführt, hilft Incident Management (Vorfallmanagement), Ausfallzeiten zu reduzieren, Kosten im Griff zu behalten und das Vertrauen von Mitarbeiter:innen und Kund:innen aufrechtzuerhalten.
Wenn Probleme auftreten, gibt Ihnen die Zendesk Vorfallmanagement-Software Ihrem Team die Struktur und Tools, um schnell zu handeln, organisiert zu bleiben und klar mit allen Beteiligten zu kommunizieren. Von intelligenten Ticketing-Workflows bis hin zu Berichten und Analysen hilft Zendesk Ihnen dabei, Störungen in eine Gelegenheit zu verwandeln und Vertrauen aufzubauen.
Entdecken Sie, wie Zendesk Ihr Incident Management mit einer kostenlosen Testversion heute verbessern kann, und erleben Sie, wie die richtigen Tools die Reaktion Ihres Teams auf IT-Störungen transformieren können.
