Beitrag • 4 Min. Lesezeit
Agentische KI vs. generative KI: Die wichtigsten Unterschiede
Sowohl agentische KI als auch generative KI spielen eine wichtige Rolle bei der Automatisierung von CX-Aufgaben und der Verbesserung von Kundeninteraktionen. Erfahren Sie, wie sich agentische KI vs. generative KI unterscheiden und wo jede den größten Mehrwert bietet.
Zuletzt aktualisiert: 30. September 2025
Wenn die meisten Menschen den Begriff Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) hören, denken sie an Tools wie ChatGPT oder Google Gemini. Diese bekannte Technologie, die als generative KI bezeichnet wird, hat große Aufmerksamkeit erregt, weil sie menschliche Kreativität und Kommunikation nachahmen kann. Doch nun entsteht eine neue Form der Intelligenz: die agentische KI. Daher fragen sich immer mehr Teams, wie sich agentische KI vs. generative KI vergleichen lassen und welche Rolle jede in ihrer Strategie spielt.
Da sich beide Technologien weiterentwickeln, beginnen sie, die KI am Arbeitsplatz neu zu gestalten. Unternehmen erforschen, wie diese Tools zusammenarbeiten können, um Effizienz und Kundenerlebnis bei jeder Interaktion zu verbessern. Diese Erkundung beginnt mit dem Verständnis, wie sich agentische KI und generative KI unterscheiden – und was das für Teams bedeutet, die vorausbleiben wollen. Genau darum geht es in diesem Leitfaden.
Mehr in diesem Leitfaden:
- Was ist agentische KI?
- Was ist generative KI?
- Was sind die Unterschiede zwischen agentischer KI und generativer KI?
- Wie agentische KI und generative KI zusammenarbeiten
- Die Zukunft von agentischer und generativer KI
- Häufig gestellte Fragen
- Modernisieren Sie Ihren Workflow mit der Zendesk-KI
Was ist agentische KI?
Agentische KI ist Software, die eigenständig Entscheidungen treffen und Aufgaben ausführen kann, um ein bestimmtes Ziel zu erreichen. Anstatt starren, vorprogrammierten Regeln zu folgen, kann sie eigenständig eine Abfolge von Aktionen planen und durchführen.
Wichtige Merkmale der agentischen KI sind:
Autonomes Entscheiden
Zielorientierte Aufgabenausführung
Mehrstufiges Denken und Planen
Kontextbewusstsein und Anpassungsfähigkeit
Sie hören in diesem Zusammenhang möglicherweise auch den Begriff KI-Agent. Obwohl verwandt, bezeichnet ein KI-Agent typischerweise eine einzelne Komponente innerhalb eines größeren Systems, während agentische KI den gesamten Rahmen beschreibt, der diese Agenten auf ein gemeinsames Ziel ausrichtet.
Anwendungsfälle für agentische KI
Agentische KI ist besonders wertvoll für Aufgaben, die eine mehrstufige Koordination und kontinuierliche Optimierung erfordern. Hier sind einige konkrete Anwendungsfälle:
- Kundenservice: Agentische KI unterstützt Support-Teams dabei, Kundenanfragen schneller und präziser zu bearbeiten. Zendesk KI-Copilot beispielsweise unterstützt Agent:innen, indem er eigenständig häufige Probleme löst und Workflows verwaltet.
- IT Service Management (ITSM): Agentische KI automatisiert Routine-IT-Anfragen und erkennt potenzielle Probleme frühzeitig durch kontinuierliche Systemüberwachung.
- Cybersicherheit: Anstatt auf menschliche Eingaben zu warten, kann agentische KI ungewöhnliche Aktivitäten erkennen, betroffene Systeme isolieren und sofort auf neue Bedrohungen reagieren.
- Lieferkette und Logistik: Agentische KI optimiert Routen und gleicht Bestände zwischen Standorten aus, sodass die Abläufe reibungslos funktionieren.
Was ist generative KI?
Generative KI bezeichnet Modelle, die neue Inhalte wie Text, Bilder und Audio erzeugen können. Sie lernt aus großen Mengen vorhandener Daten, um Ergebnisse zu erstellen, die natürlich und menschlich wirken.
Einige Merkmale der generativen KI sind:
Erzeugt Texte, Bilder, Audio oder Code
Reagiert auf Eingaben (Prompts)
Nutzt umfangreiche Trainingsdaten
Imitiert unterschiedliche Stile oder Tonalitäten
Skaliert schnell für kreative, inhaltsintensive Aufgaben
Da generative KI so ausgelegt ist, Muster in Sprache und Medien zu replizieren, ist sie hochgradig anpassungsfähig in vielen Formaten und Stilen. Das macht sie zu einer Basistechnologie für zahlreiche Tools zur Inhaltserstellung und Kommunikation.
Anwendungsfälle für generative KI
Generative KI eignet sich hervorragend, um Inhalte zu erstellen, Informationen zusammenzufassen und Sprache für unterschiedliche Kontexte anzupassen. Nachfolgend finden Sie einige der gängigsten Anwendungsfälle im Arbeitsumfeld.
- Support-Inhalte: Zendesk bietet beispielsweise eine KI-gestützte Wissensdatenbank, die Inhalte erweitert und verfeinert, indem sie Notizen in hilfreiche Artikel verwandelt, um den Self-Service zu verbessern.
- Konversationsintelligenz: Zendesk Conversational Intelligence nutzt generative KI, um Kundeninteraktionen zu analysieren und zusammenzufassen. So erhalten Agent:innen Erkenntnisse und Gesprächszusammenfassungen, die Nachbearbeitung beschleunigen und die Servicequalität erhöhen.
- Marketing-Inhalte: Generative KI-Tools wie ChatGPT können beim Brainstorming von Überschriften, E-Mail-Kampagnen und Social-Media-Ideen helfen.
- Produktdokumentation: Generative KI kann Benutzerhandbücher und Onboarding-Materialien auf Basis interner Notizen oder technischer Vorgaben erstellen.
- Schulungsmaterialien: Sie kann maßgeschneiderte Trainingsmodule, Quizfragen und vereinfachte Erklärungen für unterschiedliche Rollen generieren.
Was sind die Unterschiede zwischen agentischer KI und generativer KI?
Auch wenn diese beiden KI-Arten oft nebeneinander eingesetzt werden, erfüllen sie unterschiedliche Rollen. Der folgende Abschnitt zeigt die wichtigsten Unterschiede in ihrer Funktionsweise.
Rolle im CX
KI im Customer Experience (CX) übernimmt viele Aufgaben. Generative KI unterstützt menschliche Agent:innen, indem sie personalisierte Antworten entwirft, Kundengespräche zusammenfasst und Help-Center-Inhalte verbessert. Sie treibt außerdem Konversations-Bots an, die vorhandenes Wissen nutzen, um natürliche, markenkonforme Antworten zu liefern.
Im Gegensatz dazu wird agentische KI eingesetzt, um gesamte Support-Prozesse zu automatisieren – sie erkennt die Art einer Anfrage, sammelt relevante Konto- oder Bestelldaten und löst das Problem ohne menschliches Eingreifen. Durch die eigenständige Ausführung mehrstufiger Aufgaben erhöht agentische KI die Lösungsgeschwindigkeit und entlastet Agent:innen bei komplexeren Fällen.
Grad der Autonomie
Was agentische KI von generativer KI unterscheidet, ist ihre Fähigkeit, ohne ständige Anweisungen zu handeln. Generative KI ist promptgesteuert, das heißt, sie reagiert auf Eingaben und erzeugt daraufhin ein Ergebnis. Auch wenn sie sehr flexibel und in kommunikationsintensiven Umgebungen nützlich ist, ist sie vollständig von externen Anweisungen abhängig.
Agentische KI hingegen kann nach der Vorgabe eines Ziels eigenständig die Initiative ergreifen. Anstatt auf einen Prompt zu warten, kann sie mehrere Schritte planen und umsetzen, Entscheidungen auf Basis des Kontexts treffen und ihre Aktionen anpassen, während sie auf die Lösung hinarbeitet.
Zugrundeliegende Technologien
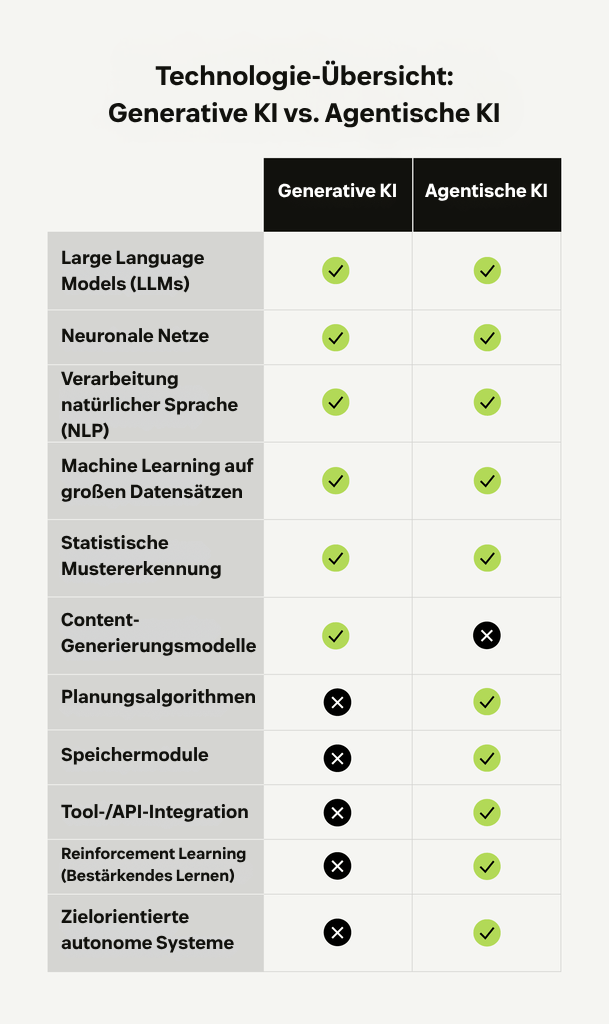
Sowohl agentische als auch generative KI basieren auf Machine Learning (ML), um aus Daten zu lernen und Muster zu erkennen. Sie unterscheiden sich jedoch darin, wie sie Large Language Models (LLMs) in ihre Systeme integrieren.
Generative KI ist nahezu vollständig auf LLMs aufgebaut, die darauf trainiert sind, Prompts zu verstehen und menschenähnliche Texte zu erzeugen. Diese Modelle nutzen Verfahren der Verarbeitung natürlicher Sprache (Natural Language Processing, NLP), um Eingaben zu interpretieren und natürlich klingende Antworten zu liefern.
Agentische KI hingegen nutzt LLMs als eine Komponente innerhalb eines größeren Systems. Während das LLM eine Anfrage interpretieren oder Teile einer Antwort generieren kann, umfasst das System zusätzlich Planungsalgorithmen und Speichermodule sowie Integrationen mit externen Tools. Zusammengenommen ermöglichen diese Technologien der agentischen KI, Entscheidungen zu treffen, den Kontext zu bewahren und komplexe Aufgaben autonom auszuführen.
Komplexität und Koordination
Man kann sich generative KI wie eine talentierte Autor:in vorstellen, die Antworten auf einzelne Prompts verfasst und dabei jeweils ein fokussiertes Ergebnis produziert. Jede Interaktion ist unabhängig, ohne dass mehrere Schritte koordiniert oder langfristige Kontexte berücksichtigt werden. Das ist besonders hilfreich für Aufgaben wie das Zusammenfassen von Texten oder das Erstellen von E-Mails.
Wenn generative KI eine Autor:in ist, dann ist agentische KI die Projektleitung. Denn sie kann weitaus komplexere Aufgaben übernehmen, die Koordination über mehrere Schritte hinweg erfordern. So kann sie beispielsweise einen kompletten Kundensupport-Fall betreuen – von der ersten Anfrage bis hin zur endgültigen Lösung.
Wie agentische KI und generative KI zusammenarbeiten
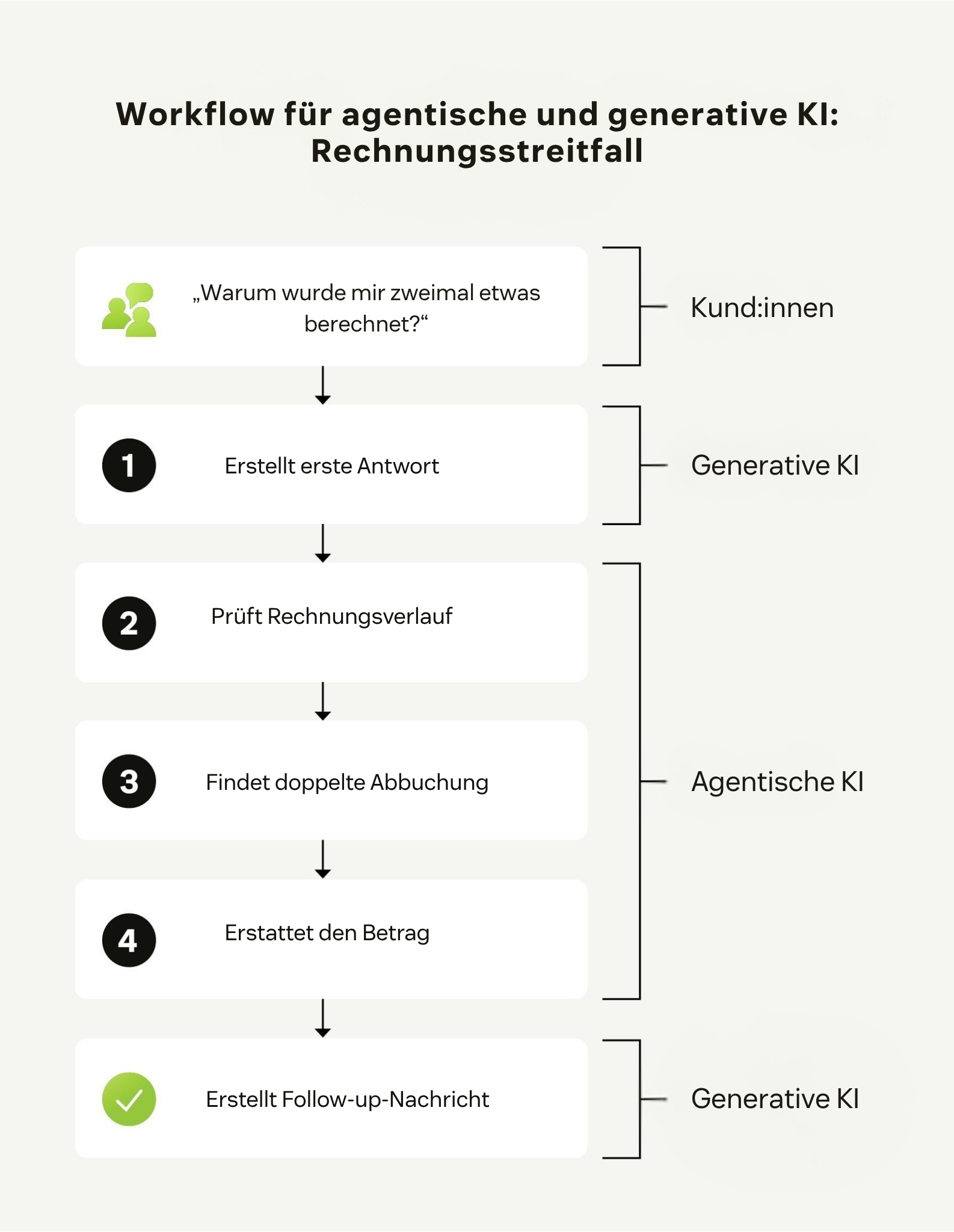
Generative KI transformiert den Kundenservice, indem sie personalisierte Interaktionen in großem Maßstab ermöglicht. Durch die Ergänzung mit agentischer KI können Unternehmen die Stärken beider Modelle kombinieren, um komplexere Prozesse von Anfang bis Ende zu automatisieren.
Agentische KI-Systeme nutzen generative KI oft als Werkzeug innerhalb größerer Workflows. Beispielsweise kann agentische KI bei der Lösung eines komplexen Falls eine Rückerstattung einleiten, interne Systeme aktualisieren und anschließend ein generatives Modell aktivieren, das eine Follow-up-Nachricht für die Kund:innen erstellt. Diese dynamische Koordination ermöglicht es Unternehmen, ein hohes Maß an Personalisierung beizubehalten, während sie gleichzeitig die Hintergrundarbeit automatisieren, die für eine schnelle und konsistente Problemlösung erforderlich ist.
Gemeinsam beschleunigen diese KI-Modelle die Lösungszeiten und steigern die Intelligenz von Agent:innen, sodass Teams sich auf höherwertige Aufgaben konzentrieren können.
Die Zukunft von agentischer und generativer KI
Mit Blick in die Zukunft wird KI am Arbeitsplatz zunehmend auf die Zusammenarbeit von agentischer und generativer KI setzen, um Produktivität und Mitarbeiterzufriedenheit zu steigern. Da diese Technologien mehr Routinekommunikation und -aufgaben übernehmen, können menschliche Agent:innen sich auf wertvollere Interaktionen konzentrieren.
Zentrale Trends, die ihre Zukunft im CX-Bereich prägen, sind:
- Wachsender Fokus auf agentische KI: Während generative KI wichtig bleibt, werden mehr Organisationen agentische KI priorisieren, um größere operative Wirkung zu erzielen.
- Vereinheitlichte KI-gestützte Workflows: Generative und agentische KI werden in gemeinsame Workflows eingebettet, um reibungslosere Automatisierungen entlang der gesamten Customer Journey zu ermöglichen.
- Verbesserte Genauigkeit und Relevanz: Da agentische KI-Systeme aus Interaktionen lernen und sich anpassen, werden zukünftige Lösungen immer präzisere Maßnahmen zur Erfüllung der Kundenerwartungen entwickeln.
- Stärker personalisierte Erlebnisse: Fortschritte in der generativen KI ermöglichen kontextbewusstere, adaptive Inhaltserstellung. Gleichzeitig koordiniert agentische KI Echtzeit-Workflows, um maßgeschneiderten und proaktiven Kundenservice in großem Maßstab zu liefern.
- Ausweitung auf proaktive Anwendungsfälle: Mit zunehmender Entwicklung orchestriert agentische KI komplexere Workflows, die die Vorhersagen der generativen KI integrieren. So können Unternehmen rechtzeitig proaktiv handeln und Probleme verhindern, bevor Kund:innen diese überhaupt äußern.
- Gestärkte Agent:innen: Die nächste Generation generativer KI liefert Agent:innen intelligentere, kontextuell relevante Antwortvorschläge, während agentische KI eine wachsende Bandbreite an Routineaufgaben automatisiert – so können Agent:innen sich auf komplexe und sensible Interaktionen konzentrieren.
Da die Investitionen in KI steigen, stellt sich für Unternehmen nicht mehr die Frage, ob sie agentische und generative KI einsetzen, sondern wie sie diese strategisch implementieren. Letztlich hängt der Erfolg davon ab, Lösungen zu wählen, die den besonderen Anforderungen Ihres CX gerecht werden.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Modernisieren Sie Ihren Workflow mit der Zendesk-KI
KI im Kundenservice ist für Unternehmen, die Kundenerwartungen erfüllen und erstklassige Erlebnisse bieten möchten, unverzichtbar geworden. Da agentische und generative KI sich rasant weiterentwickeln, hängt der Erfolg davon ab, Lösungen auszuwählen, die fortschrittliche KI nahtlos in komplexe Kundenservice-Workflows integrieren können.
Durch die Nutzung der Stärken von agentischer und generativer KI ermöglicht Zendesk-KI sofortige, personalisierte Lösungen, die die Produktivität von Agent:innen steigern und die Kundenzufriedenheit erhöhen. Speziell für Customer Experience entwickelt, versteht sie die besonderen Anforderungen von Service-Interaktionen und liefert kontextbewusste Unterstützung – damit Ihr Team sich auf das konzentrieren kann, was wirklich zählt.
